Avalanche
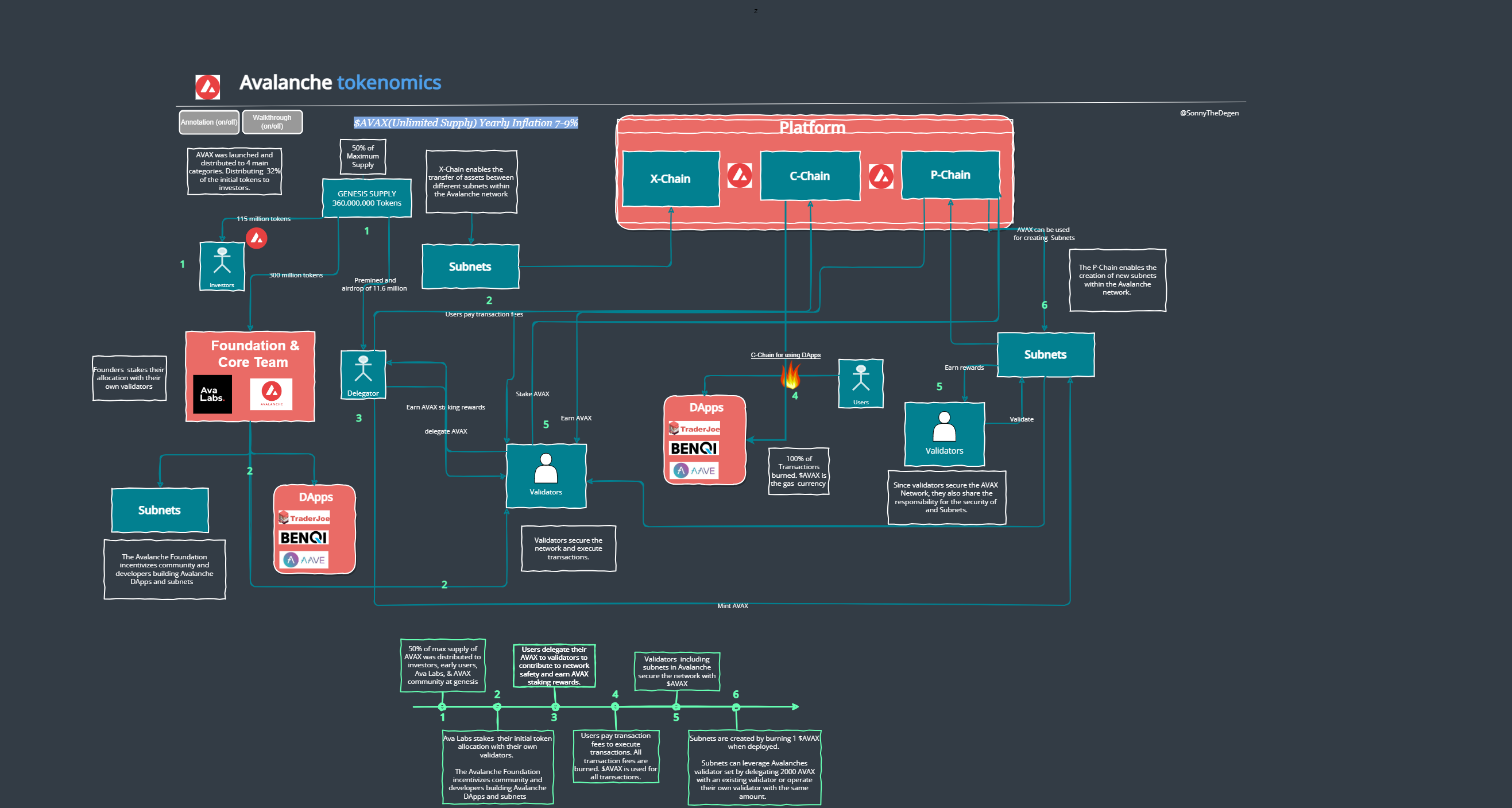
Avalanche is a groundbreaking, open-source blockchain that seamlessly caters to the requirements of both users and developers. With its modular and customizable design, Avalanche empowers developers to create highly scalable and high-performance smart contract blockchains. This innovation paves the way for a wide range of decentralized finance applications and enterprise blockchain solutions within a single, interconnected ecosystem. Avalanche introduces Subnets, enabling the creation of personalized networks featuring unique virtual machines and intricate validator rulesets. These Subnets form a platform of platforms, envisioning a global marketplace called 'The Internet of Finance,' where thousands of public and private Subnets converge. At the heart of the Avalanche platform lies AVAX, its native token, which plays a vital role in securing the network. AVAX is utilized for staking, facilitating peer-to-peer transactions, paying transaction fees, and establishing a common unit of account across multiple subnetworks created on Avalanche.
Categories:
Blockchain
Layer1
Updated:
2024-02-21
Tags:
Cross-Chain
Proof of Stake
Ticker:
AVAX
Token Strength.
Token Utility:
The $AVAX token serves four primary functions: -Pay Gas Fees -Stake and delegate to participate in the PoS consensus. -Validators on both the Avalanche Mainnet and Subnets are required to stake at least 2000 AVAX to participate in the network consensus. - Unit of account, medium of exchange, or store of value.
Demand Driver:
People use Avalanche C Chain because it’s cheap, reliable, decentralized & secure → Usage drives up C-Chain fees → Apps migrate to subnets → New validators lock up AVAX, lowering supply → C-Chain utilization drops → C-Chain gets cheaper -> Repeat
Value Creation:
-Avalanche is a payment network and foundation to create and secure subnets, which are sovereign blockchains on Avalanche. -For end-users, Avalanche offers a platform with low transaction fees and quick transaction times, which can be particularly beneficial for activities like trading digital assets or participating in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Its support for interchain compatibility also makes it easier for users to interact with multiple blockchain platforms. -The more users delegate their $AVAX to validators, the more secure the network is. -The ecosystem gains more value with each new subnet and user. -More Transactions on the Avalanche network, the more tokens are burned. This mechanism hopes to capture scarcity while offsetting inflation.
Value Capture:
Value Accrual to the $AVAX Token - AVAX is the native token of the Avalanche blockchain and is used to secure the network through staking, pay for fees, and provide a basic unit of account between multiple subnetworks created on the Avalanche platform. - The Avalanche network burns all transaction fees, lowering the effective supply. Over 4.1 million AVAX have been burned since mainnet launch. Fee burning has grown exponentially with increased network usage. - Avalanche's "Subnet" technology allows for horizontal scaling by isolating high-traffic dapps, reducing the load on the main C-chain, and lowering gas costs for all users. However, this results in short-term reduced AVAX fee burning via the C-chain. Value Accrual to the Avalanche Protocol - Validating a subnet requires validating the C-chain. Validating a subnet requires staking a minimum of 2,000 AVAX. As more subnets launch, more AVAX will be staked. - The feedback loop of increased usage driving higher fees and subnet creation, requiring more validators and staking, can lead to a reduction in overall AVAX supply availability over time. This scarcity could drive up valuation.
Business Model:
The business model for Avalanche: Revenue comes from: Transaction fees are paid by users of the network. 100% of transaction fees are burned to manage inflation for AVAX). Revenue is denominated in: $AVAX, the native token of the Avalanche platform. Revenue goes to: Validators who approve transactions and provide economic security, which is paid via new issuance of AVAX tokens (inflation) — which can be offset by the burned tokens, making the network deflationary during periods of high on-chain usage. Stakers also receive inflation for staking and securing the network. The percentage varies depending on the current level of staking participation but is currently around 7.5% annually.
Loading
Protocol Analysis.
| Problems & Solutions | Problems: #1 Scalability and Speed: Older Proof-of-Work blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and sluggish Proof-of-Stake Blockchains like Ethereum can only process 7 and 25 transactions per second, respectively. Compared to centralized financial service providers like Visa, which can handle up to 65,000 transactions at the same time, these platforms seem too slow and incapable of accommodating a large user base. #2 Interoperability: One of the problems Layer 1 Blockchains face is the lack of interoperability. Although new blockchain ecosystems are emerging daily, each with its own unique solutions to different problems, most of them cannot communicate with each other. This seriously limits their functionality. #3 Customizability: Developers often face limitations when trying to build custom solutions on existing blockchain platforms. Being bound by the rules set forth by a specific blockchain imposes certain constraints on developers, limiting their ability to customize the blockchain according to their specific requirements. This lack of flexibility can hinder the development of tailored solutions and innovative use cases. Solutions: #1 Scalability and Speed: Avalanche addresses the scalability issue by providing a platform that scales infinitely and finalizes transactions regularly in less than one second. Its unique consensus protocol and Subnet infrastructure enable high scalability. The Avalanche platform currently processes up to 4,500 transactions every second. #2 Interoperability: Avalanche allows developers to build application-specific blockchains with complex rulesets or build on existing private or public Subnets in any language. This provides a high degree of customizability and interoperability. #3 Customizability: Developers can create a subnet where each validator has specific properties. For example, one can create a subnet where each validator is located in a certain jurisdiction or where each validator is bound by some real-world contract. This may be beneficial for compliance reasons. |
|---|---|
| Predecessors | Ethereum - A Proof-of-Stake blockchain that powers decentralized applications (dApps) through smart contracts, without being controlled by a centralized entity. As the first blockchain to feature smart contracts, it has the largest ecosystem of decentralized applications, ranging from decentralized exchanges to crypto lending and borrowing platforms and more. Cosmos Network - A decentralized network of interconnected independent blockchains, allowing them to communicate and transact with each other. Polkadot - A multi-chain network that allows different blockchain networks to connect and communicate with each other. Solana - A high-performance blockchain platform that uses a unique consensus algorithm to enable fast and secure transactions at scale. |
Investment Take
... coming soon
Tokenomics Timeline.
2020-09-21
Avalanche Launch
Avalanche mainnet went live featuring three interconnected layers: the Platform Chain (P-Chain), Exchange Chain (X-Chain), and Contract Chain (C-Chain).
2021-12-14
Subnet-EVM
Ava Labs announced its Subnet-EVM, a custom virtual machine enabling developers to deploy new EVM-compatible blockchains as Avalanche Subnets.
2022-12-13
Core Wallet
Ava Labs released Core Mobile, a wallet browser extension for the Avalanche ecosystem, with support for EVM-compatible blockchains and Subnets.
2022-12-22
Avalanche Warp Messaging (AWM)
Ava Labs developed the XSVM with 2 basic capabilities: transferring assets on a Subnet and transferring assets between Subnets.
2023-01-05
Partnership with Shopify
Shopify (SHOP) expanded its NFT integration, allowing its merchants to begin designing, minting, and selling Avalanche NFTs.
2023-01-11
Partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS)
This allowed Avalanche to further integrate with AWS’ products for FedRAMP compliance use cases, establishing custom Subnets, or setting up Avalanche nodes.
2023-02-21
HyperSDK Launched
Avalanche unveiled HyperSDK, a framework for creating virtual machines on Avalanche.
2023-03-01
Glacier API
The Glacier API is an API service that indexes Subnets and provides real-time and historical blockchain data from Avalanche and Ethereum.
2023-04-06
Avalanche Evergreen Subnets
Enables institutions to establish private, permissioned networks for research, development, or production purposes while maintaining the ability to interact with other Subnets through AWM.
2023-04-07
Avalanche Introduces Cortina Network Upgrade
Cortina brought improvements such as X-Chain linearization, batched delegated rewards, and an increased C-Chain gas limit to mainnet.
2023-07-25
Avalanche Vista Unveiled
An initiative that aims to allocate up to $50.00 million to acquiring tokenized assets (real-world assets) issued on Avalanche.
2023-08-29
Teleporter Testnet Release
Teleporter is a cross-chain messaging tool built on AWM that will enable developers to call contracts on other EVM-compatible blockchains.
Loading
Loading
Loading
Ecosystem Users.
| Name | Role | |
|---|---|---|
| Ava Labs | AVA Labs plays a crucial role in the development, support, and growth of the Avalanche protocol. Their contributions span core development, research, ecosystem support, governance facilitation, and partnerships, all aimed at advancing the capabilities and adoption of the Avalanche platform. | |
| Avalanche Foundation | The Avalanche Foundation is an active and cornerstone member and supporter of the Avalanche community. It contributes to the continuing development, implementation, and maintenance of the Avalanche public network and the Avalanche community by funding (through grants and investments), publicizing, and otherwise encouraging the development and implementation of different types of software, staking tokens and operating nodes/validators, creating content, and generally being a resource to the Avalanche community. | |
| Delegators & Validators | The $AVAX token is used to participate in the network through staking. Users with at least 2,000 AVAX tokens staked on the network can run a validator node, while the minimum staking requirement to become a delegator is 25 AVAX. The minimum lock-up period is 14 days, and the staking rewards are around 8.5% for both parties. | |
| Developers | Developers play a crucial role in the success of the Avalanche ecosystem. They can build and implement different types of software, such as smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), Subnets, APIs, utilities, upgrades, bridges to other blockchains, and wallet software. | |
| General Users | They use the Avalanche platform to create and transfer digital assets or communicate with dApps powered by smart contracts. | |
| Investors | Typically those who buy and hold AVAX tokens with the expectation of potential future returns. |